How to Stop Sensitive Teeth Pain Immediately
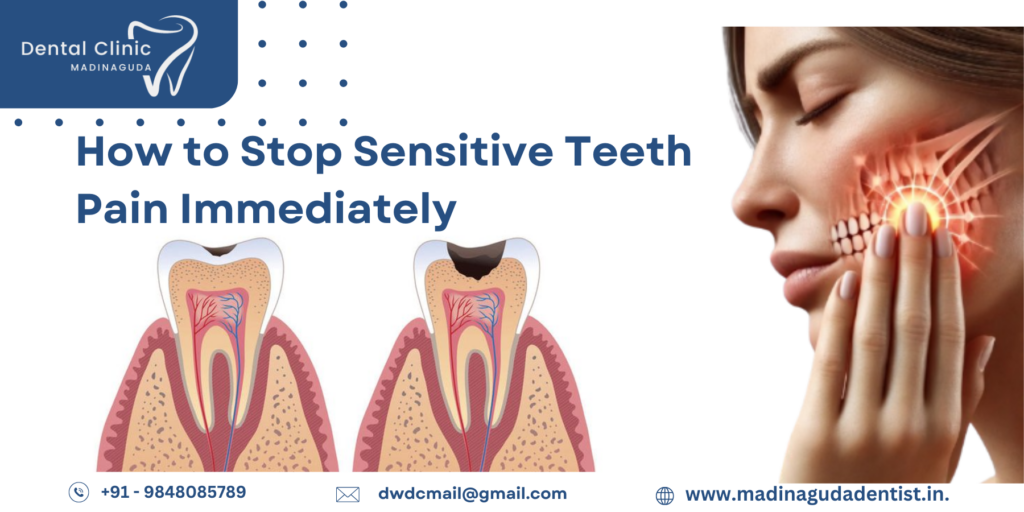
How to Stop Sensitive Teeth Pain Immediately? Use desensitizing toothpaste, fluoride rinse, or saltwater rinse to ease discomfort. Avoid hot, cold, or acidic foods that trigger pain. Applying a cold compress can also help. For lasting relief, visit Madinaguda Dentist Hospital, where Dr. Lakshmi offers expert treatments like fluoride applications and dental bonding to protect your teeth and reduce sensitivity effectively.
What Is Tooth Sensitivity?
Tooth sensitivity is a common dental problem that causes sharp pain or discomfort when eating or drinking hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods. It can also happen while brushing, flossing, or breathing in cold air. This occurs when the protective enamel layer wears down or when gum recession exposes the dentin, which contains tiny nerve endings.
Causes of Tooth Sensitivity
Enamel erosion: Caused by acidic foods, sugary drinks, and teeth grinding.
Gum recession: Due to aging, aggressive brushing, or gum disease.
Cavities and tooth decay: Expose the inner layers of the tooth, leading to pain.
Cracked or damaged teeth: Can create pathways to the nerves, causing sensitivity.
Teeth whitening treatments: Some whitening products weaken enamel temporarily.
How to Manage and Prevent Tooth Sensitivity?
Use desensitizing toothpaste: Helps block pain signals from reaching nerves.
Brush gently with a soft-bristled toothbrush: Avoids further enamel loss.
Limit acidic and sugary foods: Protects enamel from erosion.
Floss daily: Removes plaque and prevents gum recession.
Visit Madinaguda Dentist Hospital: Get expert dental care and personalized treatment.
What causes sudden tooth sensitivity?

Receding gums
Receding gums occur when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back, exposing the tooth roots. Unlike the enamel-covered part of the tooth, the roots lack protection, making them more sensitive and prone to decay. Gum recession can worsen over time, leading to discomfort and serious dental issues if left untreated.
Causes of Receding Gums
Aggressive brushing – Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can wear down gum tissue.
Poor oral hygiene – Plaque buildup and tartar can lead to gum disease and recession.
Gum disease (Periodontal disease) – Bacterial infections weaken the gums and cause them to recede.
Aging – As people age, gums naturally recede, increasing sensitivity.
Teeth grinding (Bruxism) – Constant pressure on teeth can weaken gums over time.
Tobacco use – Smoking or chewing tobacco reduces blood flow to the gums, making them more vulnerable.
Genetics – Some people are naturally more prone to gum recession due to hereditary factors.
Symptoms of Receding Gums
Increased tooth sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet foods.
Longer-looking teeth due to exposed roots.
Gum inflammation, swelling, or bleeding, especially while brushing or flossing.
Loose teeth in severe cases, as the gum tissue no longer holds them securely.
How to Prevent and Manage Receding Gums
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and brush gently to avoid damaging gum tissue.
- Maintain proper oral hygiene by brushing twice a day and flossing regularly.
- Visit your dentist regularly to detect early signs of gum disease and receive professional cleaning.
- Use fluoride toothpaste to strengthen teeth and reduce sensitivity.
- Wear a mouthguard if you grind your teeth to prevent further damage.
- Quit smoking and tobacco use to improve gum health.
- Consider gum grafting for severe cases, where a dentist restores gum tissue through surgery.
Cracked tooth
How to Stop Sensitive Teeth Pain Immediately? A cracked tooth can cause pain and sensitivity, making eating and drinking uncomfortable. At Madinaguda Dentist Hospital, Dr. Lakshmi provides expert care to prevent severe dental issues like infections and decay. Seeking prompt treatment can help relieve discomfort and protect your oral health.
Causes of a Cracked Tooth
Biting hard foods – Chewing on ice, hard candies, or nuts can cause cracks.
Teeth grinding (Bruxism) – Constant grinding can weaken and crack teeth over time.
Injury or trauma – Accidents, falls, or sports injuries can result in cracks.
Temperature changes – Sudden shifts from hot to cold foods can weaken enamel.
Large fillings or weakened teeth – Older dental work or cavities can increase the risk of cracks.
Symptoms of a Cracked Tooth
- Sensitivity to hot, cold, or sweet foods due to exposed inner layers.
- Pain when chewing or biting, especially when pressure is applied.
- Swelling or irritation in the gums near the affected tooth.
- Intermittent discomfort that comes and goes.
Why a Cracked Tooth Needs Immediate Attention
The crack can allow bacteria to enter, leading to infections and decay.
It may worsen over time, leading to tooth loss if untreated.
Early treatment can prevent complications and reduce pain.
Treatment Options for a Cracked Tooth
- Dental bonding – A filling material is applied to seal minor cracks.
- Dental crowns – A cap covers and protects larger cracks.
- Root canal treatment – If the crack extends to the pulp, a root canal may be necessary.
- Tooth extraction – In severe cases, the tooth may need to be removed and replaced.
Preventing Cracked Teeth
Avoid chewing on hard objects like ice or pens.
Use a mouthguard if you grind your teeth at night.
Wear a protective mouthguard during sports activities.
Maintain good oral hygiene to keep teeth strong and healthy.
Tooth decay
Tooth decay occurs when bacteria in the mouth break down sugars from food, producing acids that gradually erode the tooth enamel. This weakens the protective layer of the tooth, exposing the inner dentin and nerves, leading to increased tooth sensitivity and discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods. If left untreated, decay can cause cavities, infections, and even tooth loss.
Causes of Tooth Decay
Poor oral hygiene – Not brushing and flossing regularly allows plaque buildup, which leads to decay.
Sugary and acidic foods – Consuming sweets, sodas, and acidic foods weakens enamel over time.
Plaque buildup – Bacteria in plaque produce acid that slowly destroys the enamel and dentin.
Dry mouth – Reduced saliva flow makes it harder to wash away bacteria and food particles.
Lack of fluoride – Fluoride strengthens enamel and helps prevent cavities.
Grinding teeth (Bruxism) – Constant pressure can wear down enamel and increase decay risk.
Symptoms of Tooth Decay
Tooth sensitivity when consuming hot, cold, or sugary foods.
Visible holes or dark spots on the surface of the teeth.
Toothache or mild pain that worsens over time.
Bad breath and an unpleasant taste in the mouth due to bacteria buildup.
Swelling or pus formation in severe cases, indicating an infection.
How to Prevent and Manage Tooth Decay
- Brush twice a day using fluoride toothpaste to strengthen enamel.
- Floss daily to remove food particles and plaque between teeth.
- Reduce sugary and acidic foods to minimize bacterial growth.
- Drink plenty of water to wash away food debris and bacteria.
- Use fluoride treatments or mouthwash to protect against cavities.
- Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and professional cleanings.
- Consider dental sealants to provide an extra layer of protection on molars.
Dental procedures
Sensitive teeth can cause discomfort when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods. Fortunately, dental treatments can help reduce sensitivity, strengthen enamel, and protect exposed tooth roots. Your dentist can determine the best treatment based on the severity and underlying cause of your sensitivity.
Common Dental Procedures for Sensitive Teeth
Fluoride Treatments
A professional fluoride application strengthens enamel and reduces sensitivity.
Available as gels, varnishes, or foams applied at the dental clinic.
Helps rebuild weak enamel and protect against cavities.
Desensitizing Agents
- Special desensitizing pastes or varnishes block nerve signals in sensitive teeth.
- Provides relief from pain caused by temperature changes or acidic foods.
- Can be applied at the dental clinic or used in prescription toothpaste.
Dental Bonding
A tooth-colored resin is applied to exposed dentin or receding gums.
Protects the sensitive areas and prevents further enamel erosion.
A quick and painless procedure offering long-lasting relief.
Gum Grafts
- Recommended for severe gum recession that exposes tooth roots.
- Tissue from another part of the mouth is grafted onto the receding gum area.
- Helps cover the exposed roots and reduces sensitivity.
Dental Sealants
A protective coating applied to the chewing surfaces of teeth.
Prevents further enamel erosion and protects against decay.
Commonly used for molars and premolars to reduce sensitivity.
Root Canal Therapy
- Used when sensitivity is caused by deep decay or nerve damage.
- Removes the infected pulp and seals the tooth to eliminate pain.
- Provides a permanent solution for extreme sensitivity.
When to See a Dentist?
If your tooth sensitivity lasts for several weeks and worsens over time.
When over-the-counter sensitivity toothpaste does not provide relief.
If you experience sharp pain while eating or drinking.
When you have visible gum recession or exposed tooth roots.
Brushing too hard
Brushing your teeth is essential for good oral health, but brushing too hard can cause more harm than good. Applying excessive pressure while brushing can damage your enamel and gums, leading to increased tooth sensitivity and other dental problems.
Effects of Brushing Too Hard
Enamel Erosion
The outer layer of your teeth (enamel) protects against decay and sensitivity.
Brushing too hard gradually wears down the enamel, making teeth more vulnerable.
Weakened enamel can lead to increased sensitivity and a higher risk of cavities.
Gum Recession
- Harsh brushing can cause gums to pull away from the teeth, exposing the roots.
- Exposed roots lack enamel protection, making them highly sensitive to hot, cold, and sweet foods.
- Receding gums can also increase the risk of gum disease and tooth loss if left untreated.
Tooth Sensitivity
When enamel wears down, the dentin layer (which contains tiny nerve endings) gets exposed.
This makes teeth more sensitive to temperature changes and certain foods.
Sensitivity can cause discomfort when eating or drinking hot, cold, or acidic items.
How to Brush Gently Without Causing Damage
Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush
- Soft bristles clean effectively without damaging the enamel or gums.
- Replace your toothbrush every three months or when bristles become frayed.
Apply Gentle Pressure
- Hold your toothbrush lightly, like a pencil, and avoid pressing too hard.
- Use short, gentle strokes rather than aggressive scrubbing motions.
Use the Right Technique
- Brush at a 45-degree angle to your gums for the best cleaning.
- Move the brush in small, circular motions instead of back-and-forth scrubbing.
Choose a Non-Abrasive Toothpaste
- Some whitening or charcoal-based toothpaste can be too abrasive.
- Use a fluoride toothpaste that protects enamel without being too harsh.
Consider an Electric Toothbrush
Many electric toothbrushes have pressure sensors to prevent brushing too hard.
They provide consistent and gentle cleaning for better oral health.
When to See a Dentist?
- If you notice increased tooth sensitivity or gum recession.
- If your gums bleed frequently while brushing.
- If you experience tooth pain or discomfort that doesn’t go away.
Gum recession
Gum recession occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth pulls back or wears away, exposing the roots. This condition can lead to pain, sensitivity, and an increased risk of tooth decay. If left untreated, gum recession can worsen over time, potentially leading to gum disease and tooth loss.
Causes of Gum Recession
Aggressive Brushing
- Brushing too hard or using a hard-bristled toothbrush can damage gum tissue over time.
- This can lead to gum shrinkage and expose the sensitive roots of the teeth.
Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease)
- Bacterial infections weaken the gum tissue, causing it to recede.
- Poor oral hygiene can lead to plaque and tartar buildup, increasing the risk of gum disease.
Genetics
- Some people are genetically prone to gum recession, even with proper dental care.
- If a family member has receding gums, you may be more likely to experience it.
Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
- Clenching or grinding your teeth can put excessive pressure on gums, leading to recession.
- Wearing a nightguard can help prevent damage from grinding.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
Tobacco products cause gum inflammation and reduced blood flow, leading to gum deterioration.
Smokers are at a higher risk of severe gum recession and tooth loss.
Poor Dental Care
- Irregular brushing, flossing, and missing dental check-ups can allow plaque buildup, causing gum disease and recession.
Causes of Gum Recession
Tooth Sensitivity
- Exposed roots lack enamel protection, making teeth more sensitive to hot, cold, and sweet foods.
Increased Risk of Cavities
- Without gum protection, the roots are more prone to decay and cavities.
Aesthetic Concerns
- Receding gums can make teeth appear longer and uneven, affecting your smile.
Loose Teeth and Tooth Loss
- Severe gum recession can lead to weak or unstable teeth, increasing the risk of tooth loss.
How to Prevent Gum Recession
Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush
- Gentle brushing prevents gum damage while keeping teeth clean.
Adopt Proper Brushing Techniques
Hold your toothbrush at a 45-degree angle and use small circular motions.
Avoid harsh scrubbing or using too much pressure.
Floss Daily
- Flossing removes plaque from areas your toothbrush can’t reach, preventing gum disease.
Quit Smoking and Tobacco Use
- Stopping smoking improves gum health and reduces the risk of further recession.
Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Professional cleanings and check-ups at Madinaguda Dentist Hospital can help detect and manage gum issues early.
Treatments like scaling, root planing, and gum grafts may be recommended in severe cases.
Gum disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common infection of the gums caused by plaque buildup on the teeth. If left untreated, it can lead to gum recession, tooth sensitivity, and even tooth loss. Maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental checkups are essential to prevent and manage gum disease.
Causes of Gum Disease
Plaque and Tartar Buildup
Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria, food particles, and saliva that forms on teeth.
If not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which irritates the gums.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Infrequent or improper brushing and flossing allow harmful bacteria to thrive, increasing the risk of gum disease.
Smoking and Tobacco Use
- Tobacco weakens the immune system, making it harder for the gums to fight infections.
- Smokers are at a higher risk of developing severe gum disease and tooth loss.
Medical Conditions
- Diabetes, heart disease, and hormonal changes (such as pregnancy) can make gums more vulnerable to infection.
Genetics
- Some people are genetically prone to gum disease, even with good oral hygiene.
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Red, Swollen, or Bleeding Gums
- Healthy gums should be firm and pink. Infected gums may bleed while brushing or flossing.
Persistent Bad Breath (Halitosis)
- Bacteria buildup in the mouth produces a foul odor, even after brushing.
Receding Gums
- Gums pulling away from teeth is a sign of advancing gum disease.
Tooth Sensitivity and Pain
- Exposed tooth roots can cause pain when eating hot, cold, or sweet foods.
Loose or Shifting Teeth
- As gum disease progresses, it can damage the bone supporting the teeth, making them unstable.
Prevention and Treatment of Gum Disease
Brush Twice a Day
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste to remove plaque.
Floss Daily
- Flossing helps clean between teeth where a toothbrush cannot reach.
Use an Antiseptic Mouthwash
- Mouthwash can kill bacteria and reduce plaque buildup.
Quit Smoking
- Stopping smoking improves gum health and lowers the risk of severe gum disease.
Regular Dental Checkups
- Visiting Madinaguda Dentist Hospital for professional cleanings and early detection can prevent serious gum problems.
Teeth grinding
How to Stop Sensitive Teeth Pain Immediately? Teeth grinding (bruxism) can cause sensitivity, tooth damage, and jaw pain if untreated. At Madinaguda Dentist Hospital, Dr. Lakshmi offers expert care to manage bruxism and prevent long-term dental issues. Early treatment can help protect your teeth and relieve discomfort effectively
Causes of Teeth Grinding
Stress and Anxiety
- High levels of stress or anxiety can lead to unconscious teeth grinding, especially at night.
Misaligned Teeth (Malocclusion)
- If teeth do not fit together properly, it can cause unnecessary pressure on certain teeth, leading to grinding.
Sleep Disorders
- Conditions like sleep apnea or snoring can increase the risk of bruxism.
Lifestyle Factors
- Excessive caffeine, alcohol, or smoking can trigger or worsen teeth grinding.
Medications and Medical Conditions
- Certain medications, such as antidepressants, or conditions like Parkinson’s disease, may contribute to bruxism.
Effects of Teeth Grinding
Worn Down Enamel
- Continuous grinding wears away the protective enamel, making teeth more sensitive to hot, cold, and sweet foods.
Tooth Sensitivity and Pain
- Exposed dentin due to enamel loss causes discomfort while eating or drinking.
Gum Recession and Gum Disease
- Excess pressure on teeth can weaken gums, leading to gum recession and potential infections.
Jaw Pain and TMJ Disorders
- Grinding puts stress on the jaw muscles and joints, causing pain and stiffness.
Headaches and Ear Pain
- Frequent clenching can lead to tension headaches and ear discomfort.
Prevention and Treatment for Teeth Grinding
Use a Mouthguard
- A custom-made mouthguard from Madinaguda Dentist Hospital can help protect your teeth at night.
Manage Stress and Anxiety
- Relaxation techniques, meditation, and counseling can help reduce stress-related grinding.
Correct Dental Misalignment
- If grinding is caused by uneven teeth, orthodontic treatments may help.
Limit Stimulants
- Reduce caffeine, alcohol, and smoking to lower the risk of bruxism.
Practice Jaw Exercises
- Strengthening and relaxing jaw muscles can help reduce tension and prevent grinding.
Teeth whitening products
Teeth whitening products, such as whitening gels, strips, and toothpaste, are designed to remove stains and brighten your smile. They contain bleaching agents like hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide, which help break down surface stains. While effective, excessive or improper use can lead to tooth sensitivity, enamel erosion, and gum irritation.
How Teeth Whitening Products Work
Whitening Toothpaste
- Contains mild abrasives and chemicals that polish teeth and remove surface stains.
Whitening Strips and Gels
- These contain peroxide-based bleaching agents that penetrate enamel to lighten deep stains.
Whitening Trays
- Custom-fitted trays with whitening gel offer stronger and longer-lasting results.
Potential Risks of Overusing Whitening Products
Tooth Sensitivity
- Frequent whitening can wear down enamel, exposing the dentin layer and leading to pain when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods.
Gum Irritation
- Strong bleaching agents can cause redness and irritation if they come into contact with gums.
Enamel Erosion
- Excessive whitening can weaken enamel, making teeth more prone to cavities and decay.
Uneven Whitening
- Overuse may lead to patchy or unnatural-looking results, especially if teeth have fillings or crowns.
Safe Teeth Whitening Tips
Follow Product Instructions
- Use whitening products only as directed to avoid overuse and sensitivity.
Choose Dentist-Approved Products
- Look for whitening products with the ADA Seal of Acceptance for safe and effective results.
Limit Whitening Frequency
- Avoid excessive use—whitening every 6 months to a year is usually sufficient.
Use Fluoride Toothpaste
- Helps strengthen enamel and reduce sensitivity after whitening treatments.
Visit a Dentist for Professional Whitening
- Madinaguda Dentist Hospital offers safe, effective whitening treatments tailored to your needs.
Age
As we age, our teeth go through natural changes that can lead to increased sensitivity and other dental issues. Over time, the protective enamel layer gradually wears down, exposing the softer inner layer called dentin. This makes teeth more vulnerable to hot, cold, sweet, and acidic foods, leading to discomfort or pain. Additionally, gums may recede with age, exposing the sensitive tooth roots, further contributing to sensitivity.
Effects of Aging on Teeth
Enamel Wear
- Years of chewing, grinding, and exposure to acidic foods cause enamel to thin, making teeth more sensitive.
Gum Recession
- As gums naturally recede, they expose the tooth roots, which lack enamel protection and are highly sensitive.
Increased Risk of Cavities
- Worn enamel and gum recession can increase the chances of decay, leading to more sensitivity.
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
- Aging and certain medications can reduce saliva production, causing dry mouth, which weakens enamel and makes teeth more prone to sensitivity.
Tips to Protect Your Teeth as You Age
Use Fluoride Toothpaste
- Strengthens enamel and reduces sensitivity.
Brush Gently with a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush
- Prevents further enamel wear and gum recession.
Floss Daily
- Helps remove plaque and protects gum health.
Stay Hydrated
- Drinking plenty of water helps combat dry mouth and keeps teeth healthy.
Avoid Acidic and Sugary Foods
- Limits enamel erosion and reduces the risk of sensitivity.
Use a Mouthguard if You Grind Your Teeth
- Protects enamel from wear and tear.
Visit Your Dentist Regularly
- Routine dental checkups at Madinaguda Dentist Hospital help detect and prevent age-related dental issues.
Plaque buildup
Plaque buildup is a sticky film of food particles and bacteria that forms on your teeth. If not removed properly, it can harden into tartar, leading to gum disease, cavities, and sensitivity. Over time, plaque damages enamel and irritates the gums, causing inflammation and infection.
How Plaque Buildup Affects Your Teeth and Gums
Weakens Tooth Enamel
- Plaque contains harmful acids that erode enamel, making teeth more sensitive to hot, cold, and sweet foods.
Leads to Gum Inflammation (Gingivitis)
- The bacteria in plaque irritate gums, causing redness, swelling, and bleeding during brushing or flossing.
Can Cause Tartar Formation
- If not removed, plaque hardens into tartar (calculus), which cannot be cleaned with a toothbrush and requires professional dental cleaning.
Increases Risk of Cavities
- Plaque creates an acidic environment, breaking down tooth enamel and leading to painful cavities.
Can Progress to Periodontal Disease
- Severe plaque buildup can cause gum recession, infection, and even tooth loss if left untreated.
How Plaque Buildup Affects Your Teeth and Gums
Brush Twice a Day
- Use a fluoride toothpaste and brush gently for at least two minutes to remove plaque effectively.
Floss Daily
- Flossing removes food particles and bacteria from areas a toothbrush cannot reach, preventing gum irritation.
Use an Antibacterial Mouthwash
- Helps kill bacteria and reduce plaque buildup between brushings.
Limit Sugary and Starchy Foods
- Sugary and carbohydrate-rich foods feed plaque bacteria, increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Visit Your Dentist Regularly
- Professional cleanings at Madinaguda Dentist Hospital help remove hardened plaque (tartar) and keep your gums healthy.
Mouthwash use
Mouthwash is a great addition to your oral hygiene routine, but choosing the right one is essential to protect your teeth and gums. Some mouthwashes contain strong chemicals or alcohol, which can dry out your mouth, irritate sensitive teeth, and even weaken enamel with overuse. Using the wrong type of mouthwash may cause discomfort instead of providing benefits. Selecting an alcohol-free, fluoride-based mouthwash can help maintain a healthy, fresh mouth without causing sensitivity.
How Plaque Buildup Affects Your Teeth and Gums
Dry Mouth (Xerostomia)
- Alcohol-based mouthwashes reduce saliva production, leading to dry mouth and bad breath.
Increased Tooth Sensitivity
- Strong chemicals can weaken enamel, making teeth more sensitive to hot, cold, and sweet foods.
Gum Irritation
- Some ingredients cause burning or discomfort, especially for those with sensitive gums.
Disruption of Oral Bacteria Balance
- Harsh mouthwashes may kill both harmful and beneficial bacteria, which can negatively impact oral health.
How to Choose the Right Mouthwash
Opt for Alcohol-Free Mouthwash
- Helps prevent dry mouth and irritation.
Use a Fluoride-Based Mouthwash
- Strengthens enamel and protects against sensitivity and cavities.
Check for Soothing Ingredients
- Mouthwashes with aloe vera or chamomile can be gentle on sensitive gums.
Avoid Strong Chemical-Based Mouthwashes
- Choose milder formulas to avoid damaging enamel.
Tips for Proper Mouthwash Use
Use Once or Twice a Day
- Overuse can lead to sensitivity.
Swish for 30 Seconds
- This ensures the mouthwash reaches all areas for maximum benefit.
Avoid Eating or Drinking Immediately After
- Give it time to work effectively before rinsing it away.
When to Seek Professional Help?
How to Stop Sensitive Teeth Pain Immediately? While home care helps, professional treatment is sometimes necessary to prevent serious dental issues. If you have persistent pain, swelling, or bleeding, visit Madinaguda Dentist Hospital, where Dr. Lakshmi provides expert care to detect and treat problems early. Ignoring sensitivity can lead to infections, gum disease, or tooth loss, so seeking timely dental help ensures lasting relief and better oral health.
Causes of a Cracked Tooth
Signs You Need to See a Dentist
Persistent Tooth Pain
- If you have continuous or severe toothache, it may indicate decay, infection, or nerve damage.
Bleeding or Swollen Gums
- Gums that bleed while brushing or flossing could be an early sign of gum disease (gingivitis or periodontitis).
Sudden Sensitivity to Hot or Cold
- If your teeth react strongly to temperature changes, it may indicate enamel erosion, cavities, or receding gums.
Bad Breath That Won’t Go Away
- Chronic bad breath (halitosis) despite good oral hygiene could be a sign of gum disease, infections, or other underlying issues.
Swelling in the Mouth or Face
- Any lumps, sores, or swelling in the gums, cheeks, or jaw may be a sign of infection or oral health conditions that need urgent attention.
Loose or Shifting Teeth
- If your teeth feel loose or misaligned, this could be a symptom of advanced gum disease or bone loss.
Jaw Pain or Difficulty Chewing
- Persistent jaw pain, clicking, or difficulty opening your mouth could be linked to TMJ disorders or bite issues.
The 8 Worst Foods for Your Teeth
1. Sour candies
How to Stop Sensitive Teeth Pain Immediately? Sour candies are highly acidic and sugary, causing enamel erosion, cavities, and sensitivity. Their sticky texture allows bacteria to thrive, worsening dental damage. At Madinaguda Dentist Hospital, Dr. Lakshmi provides expert care to prevent and treat tooth sensitivity for a healthier smile.
High Acid Content: Sour candies contain strong acids that weaken and wear down the protective enamel, making teeth more vulnerable to decay.
Sticky Texture: Many sour candies are chewy and stick to the surface of your teeth, making it harder for saliva to wash away sugar and acid.
Sugar Feeds Bacteria: The sugar in these candies provides fuel for harmful bacteria, increasing the risk of cavities and gum disease.
Increased Sensitivity: Regular consumption of sour candies can lead to enamel thinning, causing discomfort when eating hot, cold, or sweet foods.
Difficult to Remove: Because they stick to teeth, brushing and flossing may not always remove all the candy residue, leading to long-term damage.
How to Protect Your Teeth?
If you eat sour candies, rinse your mouth with water immediately to neutralize acids.
Avoid brushing right away, as acids soften the enamel, and brushing can cause further damage.
Choose sugar-free alternatives or enjoy them in moderation to reduce the risk of tooth decay.
Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily.
2. Bread
Bread, especially white bread, may seem harmless, but it can negatively impact your dental health. When you chew bread, your saliva breaks it down into simple sugars, which stick to your teeth and create the perfect environment for cavity-causing bacteria to thrive. Over time, this can lead to plaque buildup, tooth decay, and gum problems. Here’s why bread is considered one of the worst foods for your teeth:
Turns into Sugar Quickly: White bread contains refined carbohydrates that break down into sugar almost immediately, feeding harmful bacteria in your mouth.
Sticky Texture: Soft bread easily gets stuck between your teeth and in the crevices, making it harder to remove with regular brushing.
Increases Plaque Formation: The sugars from bread combine with bacteria in your mouth, leading to plaque buildup and a higher risk of cavities.
Can Contribute to Gum Issues: Frequent consumption of refined carbs like white bread can lead to inflammation in the gums, increasing the risk of gingivitis.
Processed Bread vs. Whole Grains: White bread is more damaging compared to whole grain bread, which contains fiber that stimulates saliva production and helps clean teeth.
How to Protect Your Teeth?
Opt for whole grain bread, which is less processed and contains more fiber to reduce sugar absorption.
Drink water after eating bread to wash away food particles and prevent sugar from lingering on your teeth.
Brush and floss regularly to remove trapped food and bacteria.
Limit bread intake, especially highly processed varieties, to maintain better oral health.
3. Alcohol
Alcohol can negatively impact your teeth and gums in several ways, primarily by causing dry mouth, which reduces saliva production. Saliva is essential for washing away bacteria and food particles, helping to protect your teeth from decay. Many alcoholic drinks also contain high levels of sugar and acid, which can erode enamel and increase the risk of cavities. Here’s why alcohol is considered harmful to your dental health:
How Alcohol Affects Your Teeth?
Reduces Saliva Production: Alcohol dries out the mouth, leading to less saliva flow. Saliva plays a crucial role in neutralizing acids and protecting teeth from decay.
Leads to Bad Breath: A dry mouth creates an ideal environment for bacteria to thrive, often causing persistent bad breath.
Erodes Tooth Enamel: Many alcoholic drinks, especially cocktails and wine, are highly acidic and can gradually wear down the protective enamel on your teeth.
Increases Cavity Risk: Alcoholic beverages with added sugars, like sweet cocktails or flavored liquors, promote bacterial growth, leading to cavities.
Stains Your Teeth: Dark-colored drinks like red wine, whiskey, and beer can stain teeth over time, dulling your smile.
How to Minimize the Damage?
Drink water between alcoholic beverages to stay hydrated and reduce dry mouth effects.
Use a straw when drinking acidic or sugary alcohol to minimize direct contact with teeth.
Brush and floss regularly to remove sugar and acid buildup.
Limit alcohol intake and choose lower-sugar options to protect your teeth.
4. Carbonated drinks
Carbonated drinks, including sodas and energy drinks, can seriously harm your teeth due to their high sugar and acid content. These beverages weaken enamel, making teeth more vulnerable to cavities and decay. Even sugar-free sodas can be harmful because they contain acids that erode tooth enamel over time.
How Carbonated Drinks Affect Your Teeth?
High Acid Content: The acid in carbonated drinks gradually wears away tooth enamel, leading to increased sensitivity and a higher risk of cavities.
Excess Sugar Feeds Bacteria: Sugary sodas create the perfect environment for bacteria to thrive, producing acids that cause decay.
Leads to Tooth Discoloration: Frequent consumption of dark-colored sodas, like cola, can stain your teeth, making them appear yellow or dull.
Weakens Enamel, Making Teeth Brittle: Continuous exposure to acids from carbonated drinks can make teeth weaker, increasing the chances of cracks and fractures.
Promotes Dry Mouth: Some carbonated beverages, especially those with caffeine, can reduce saliva production, leading to dry mouth and bad breath.
How to Protect Your Teeth?
- Limit your intake of sodas and energy drinks to reduce acid exposure.
- Use a straw when drinking carbonated beverages to minimize contact with your teeth.
- Rinse your mouth with water after drinking to wash away sugars and acids.
- Wait at least 30 minutes before brushing to prevent further enamel damage.
- Choose healthier alternatives like water, milk, or natural fruit juices.
5. Ice
Chewing on ice may seem harmless, but it can seriously damage your teeth over time. Ice is extremely hard, and biting down on it can lead to cracks, chips, or fractures in your teeth. The cold temperature can also trigger sensitivity, especially if you already have weakened enamel or dental fillings.
How Chewing Ice Harms Your Teeth?
Can Crack or Chip Teeth: The hardness of ice puts excess pressure on teeth, increasing the risk of fractures or damage.
Wears Down Tooth Enamel: Continuous exposure to ice can weaken enamel, making teeth more prone to cavities and sensitivity.
Causes Sensitivity to Hot & Cold: The extreme temperature change from chewing ice can cause pain and discomfort in sensitive teeth.
Can Damage Fillings & Crowns: If you have dental work like fillings, crowns, or veneers, chewing ice can cause them to break or loosen.
Increases Risk of Gum Irritation: Hard ice pieces can cause small injuries to the gums, leading to discomfort and potential infections.
How to Protect Your Teeth?
- Avoid chewing ice completely and let it melt in your mouth if needed.
- Drink chilled beverages without ice cubes to reduce the temptation to chew.
- Use a straw to avoid direct contact between ice and teeth.
- If you crave chewing ice, consult a dentist as it may be a sign of an underlying nutritional deficiency, like iron deficiency (pica).
6. Citrus
Citrus fruits like oranges, lemons, and grapefruits are packed with vitamins and nutrients, but their high acidity can weaken tooth enamel over time. Frequent exposure to acidic foods can increase the risk of cavities and tooth sensitivity, making it essential to consume them wisely.
How Citrus Fruits Affect Your Teeth?
Erodes Tooth Enamel: The acid in citrus fruits gradually wears away the protective enamel, leaving teeth more vulnerable.
Increases Sensitivity: Exposed enamel can lead to pain and discomfort, especially when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods.
Promotes Tooth Decay: Weakened enamel makes it easier for bacteria to cause cavities and other dental problems.
Can Irritate Mouth Sores: The acidity in citrus fruits can worsen mouth ulcers or gum irritation.
How to Enjoy Citrus Fruits Without Harming Your Teeth?
Eat them in moderation to minimize prolonged acid exposure.
Drink citrus juices with a straw to reduce direct contact with teeth.
Rinse your mouth with water afterward to wash away excess acid.
Wait at least 30 minutes before brushing to avoid spreading the acid on softened enamel.
Pair citrus with other foods like cheese or nuts to help neutralize acidity.
7. Potato chips
Potato chips may be a popular snack, but their starchy nature can make them harmful to your teeth. The carbohydrates in chips break down into sugars, which can get trapped in the grooves of your teeth, feeding bacteria that cause plaque buildup and cavities.
How Potato Chips Affect Your Teeth?
Starches Turn into Sugar: Chips contain refined starch that quickly converts into sugar, promoting bacteria growth.
Easily Sticks to Teeth: The tiny particles get lodged between teeth and in deep grooves, increasing the risk of decay.
Encourages Plaque Buildup: Starch provides a food source for bacteria, leading to plaque and possible gum problems.
How to Protect Your Teeth After Eating Chips?
- Drink water after eating to wash away leftover starches.
- Floss and brush your teeth properly to remove stuck particles.
- Choose healthier snack options like nuts, cheese, or crunchy vegetables.
- Limit frequent snacking to reduce prolonged exposure to starches.
8. Dried fruits
Dried fruits may seem like a healthy snack, but they can be harmful to your teeth due to their sticky texture and high sugar content. They easily cling to your teeth, creating an ideal environment for bacteria to grow and cause cavities.
How Dried Fruits Affect Your Teeth?
Sticky Residue: The chewy texture makes dried fruits stick to teeth, increasing the risk of decay.
High in Natural Sugar: Concentrated sugars in dried fruits feed harmful bacteria, leading to plaque buildup.
Traps Bacteria Between Teeth: Tiny pieces can get stuck in hard-to-clean areas, contributing to cavities and gum problems.
How to Protect Your Teeth After Eating Dried Fruits?
- Drink water immediately to rinse away sugar and food particles.
- Brush and floss your teeth to remove sticky residues.
- Eat fresh fruits instead as they contain natural fiber that helps clean your teeth.
- Limit intake of dried fruits and consume them in moderation.
Share Your Valuable Thought
Tooth Sensitivity Prevention
How to Stop Sensitive Teeth Pain Immediately? Prevention starts with good oral hygiene. At Madinaguda Dentist Hospital, Dr. Lakshmi recommends using a soft-bristled toothbrush, avoiding aggressive brushing, and using toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth. Regular dental check-ups, limiting acidic foods, and wearing a mouthguard if you grind your teeth can help protect against sensitivity and ensure long-term relief.
Home Remedies for Sensitive Teeth

1. Desensitizing Toothpaste
Desensitizing toothpaste is specially formulated to help reduce tooth sensitivity and protect enamel. It contains active ingredients that block tiny openings in the teeth that lead to nerves, helping to prevent pain when consuming hot, cold, or sweet foods.
How Desensitizing Toothpaste Helps?
Blocks nerve signals: Special compounds like potassium nitrate or stannous fluoride help block pain signals to the nerves.
Strengthens enamel: Fluoride helps rebuild and protect the outer layer of the teeth.
Provides long-term relief: Regular use reduces sensitivity over time, making eating and drinking more comfortable.
How to Use Desensitizing Toothpaste for Best Results?
- Use it twice daily instead of regular toothpaste.
- Do not rinse immediately after brushing to allow the active ingredients to work effectively.
- Apply a small amount directly to sensitive areas before bed for extra relief.
2. Hydrogen Peroxide Mouthwash
Hydrogen peroxide mouthwash is a simple and effective home remedy for maintaining oral hygiene and reducing tooth sensitivity. It acts as a mild antiseptic, helping to kill bacteria and soothe minor gum irritation.
How to Use Hydrogen Peroxide Mouthwash Safely?
Kills harmful bacteria: Helps reduce plaque buildup and fights infection in the mouth.
Whitens teeth: Lightens stains over time, making your smile brighter.
Soothes gum irritation: Reduces inflammation and minor sores, promoting gum health.
Benefits of Using Hydrogen Peroxide Mouthwash
Dilute it properly – Mix equal parts of 3% hydrogen peroxide and water before use.
Swish for 30 seconds, then spit it out – Do not swallow.
Use it 2-3 times a week – Excessive use may irritate gums and cause discomfort.
3. Green Tea
Green tea is a natural and effective way to improve oral health. It contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory properties that help protect your teeth and gums, making it a great home remedy for tooth sensitivity.
Benefits of Green Tea for Oral Health
Fights bacteria: Helps reduce the growth of harmful bacteria in the mouth, lowering the risk of cavities.
Reduces inflammation: Soothes irritated gums and helps prevent gum disease.
Prevents bad breath: Naturally freshens breath by neutralizing odor-causing bacteria.
Strengthens enamel: Fluoride present in green tea helps make teeth stronger and more resistant to decay.
How to Use Green Tea for Sensitive Teeth?
Drink unsweetened green tea to get the best benefits without added sugar.
Use it as a mouth rinse by cooling it and swishing it around your mouth for a few seconds.
Drink it regularly to maintain healthy teeth and gums over time.
4. Honey and Warm Water
Honey and warm water work as a gentle and natural remedy for sensitive teeth. Honey has antibacterial and healing properties, while warm water helps soothe discomfort and cleanse the mouth. Together, they provide relief from tooth sensitivity and promote oral health.
Benefits of Honey and Warm Water for Sensitive Teeth
Natural antibacterial agent: Honey helps fight harmful bacteria that cause cavities and gum infections.
Reduces inflammation: Helps soothe irritated gums and sensitive teeth.
Aids in healing: Honey promotes tissue repair, helping with minor mouth sores or gum issues.
Maintains oral hygiene: Warm water helps wash away food particles and bacteria, keeping your mouth clean.
How to Use Honey and Warm Water for Sensitive Teeth?
Mix one teaspoon of honey in a glass of warm water and swish it around your mouth before spitting it out.
Use it as a mouth rinse once or twice a day to soothe sensitivity and promote healing.
Drink honey water in the morning for overall oral and digestive health benefits.
5. Capsaicin
Capsaicin is the active compound in chili peppers that gives them their heat. It has pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties, making it useful for reducing tooth sensitivity. While it may cause a mild burning sensation at first, regular use can help numb nerve pain and improve oral comfort.
Benefits of Capsaicin for Sensitive Teeth
Natural pain relief: Helps block pain signals from reaching the brain, reducing discomfort.
Anti-inflammatory properties: Helps soothe irritated gums and reduce swelling.
Improves blood circulation: Enhances healing in the affected areas of the mouth.
How to Use Capsaicin for Sensitive Teeth?
Capsaicin gel or cream: Apply a small amount to sensitive teeth or gums using a cotton swab.
Capsaicin mouth rinse: Dilute a small amount of cayenne pepper in warm water and rinse gently.
Capsaicin-infused toothpaste: Some herbal toothpastes contain capsaicin for pain relief
6. Turmeric
Turmeric is a powerful natural ingredient known for its anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. It has been used in traditional medicine for centuries to reduce pain, fight infections, and promote gum health. Its active compound, curcumin, helps soothe sensitive teeth and protect against bacteria that cause gum disease and cavities.
Benefits of Turmeric for Oral Health
Reduces gum inflammation: Helps soothe swollen or irritated gums.
Fights bacteria: Prevents plaque buildup and protects against infections.
Promotes overall gum health: Strengthens gums and supports oral hygiene.
How to Use Turmeric for Sensitive Teeth?
Turmeric paste: Mix turmeric powder with water or coconut oil and apply it to sensitive areas.
Turmeric mouth rinse: Add a pinch of turmeric to warm water and use it as a natural mouthwash.
Turmeric-infused toothpaste: Some herbal toothpaste options include turmeric for added protection.
7. Saltwater Rinse
A saltwater rinse is a quick, natural, and effective way to support oral health. It helps reduce inflammation, kill bacteria, and promote healing, making it a great home remedy for sensitive teeth and gum issues. Regular use can soothe discomfort and keep your mouth clean.
Benefits of Saltwater Rinse for Oral Health
Reduces inflammation: Helps soothe sore and swollen gums.
Kills harmful bacteria: Prevents infections and freshens breath.
Aids in healing: Speeds up recovery after dental treatments or minor injuries.
How to Use a Saltwater Rinse?
Mix ½ teaspoon of salt in a glass of warm water.
Swish the solution in your mouth for 30 seconds, then spit it out.
Use it 1-2 times a day for best results, but avoid excessive use to prevent enamel erosion.
8. Vanilla Extract
Vanilla extract is not just for baking—it has natural antibacterial and soothing properties that can help with tooth sensitivity and oral health. It can provide relief from minor discomfort and promote a fresh, clean feeling in your mouth.
Benefits of Vanilla Extract for Oral Health
Brushing too hard can wear down your enamel and cause gum recession, leading to tooth sensitivity. It exposes the softer dentin layer, making your teeth more sensitive to hot, cold, and sweet foods. To prevent this, use a soft-bristled toothbrush and gentle strokes while brushing.
Soothes tooth sensitivity: Its mild numbing effect can help reduce discomfort.
Fights bacteria: Contains antibacterial properties that help keep your mouth clean.
Provides a pleasant taste: Leaves a refreshing and comforting flavor.
How to Use Vanilla Extract for Sensitive Teeth?
Dip a cotton ball in pure vanilla extract.
Apply it gently to the affected tooth or gums for a few minutes.
Repeat as needed for relief, but consult a dentist for long-term sensitivity issues.
9. Clove Oil
Clove oil is a well-known natural remedy for tooth pain and gum discomfort. It contains eugenol, a natural compound with pain-relieving and antibacterial properties, making it effective for soothing sensitive teeth and fighting oral infections.
Benefits of Clove Oil for Oral Health
Relieves tooth pain: Acts as a natural anesthetic to numb pain and sensitivity.
Fights bacteria: Has strong antibacterial properties that help prevent infections.
Reduces inflammation: Helps soothe swollen gums and irritated tissues.
How to Use Clove Oil for Sensitive Teeth?
- Dilute a few drops of clove oil with a carrier oil (like coconut or olive oil).
- Apply the mixture to the affected tooth or gums using a cotton ball.
- Repeat as needed for relief, but consult a dentist for persistent pain.
10. Coconut Oil
Coconut oil is widely known for its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties, making it an effective natural remedy for oral health and sensitive teeth. It is commonly used for oil pulling, a traditional practice that helps remove harmful bacteria from the mouth and supports stronger, healthier gums.
Benefits of Coconut Oil for Oral Health
Fights bacteria: Helps eliminate harmful bacteria that cause plaque and bad breath.
Reduces inflammation: Soothes swollen gums and prevents gum disease.
Strengthens teeth: Creates a protective layer to reduce sensitivity and enamel erosion.
How to Use Coconut Oil for Sensitive Teeth?
- Oil Pulling: Swish 1 tablespoon of coconut oil in your mouth for about 10-15 minutes, then spit it out.
- Direct Application: Apply a small amount of coconut oil to sensitive areas for instant relief.
- Daily Routine: Use regularly for improved oral hygiene and fresher breath.
What questions should I ask my dentist?
1. What can I do to stop my tooth sensitivity pain right now?
To stop tooth sensitivity pain right now, rinse with warm salt water, use a sensitive toothpaste, or apply clove oil. Avoid hot, cold, or sweet foods to prevent more pain.
2. Are there any quick home remedies to relieve sensitive teeth?
Yes, you can rinse with warm salt water, apply clove oil, or use desensitizing toothpaste for quick relief. Avoid hot, cold, or acidic foods to prevent more pain.
3. Can using a desensitizing toothpaste help with immediate pain relief?
Yes, desensitizing toothpaste can help by blocking pain signals in the nerves. For quick relief, apply a small amount directly to the sensitive tooth.
4. Should I avoid certain foods or drinks to reduce the pain?
Yes, avoid very hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks, as they can trigger pain. Stick to lukewarm, soft foods to reduce discomfort.
5. Is it safe to take over-the-counter pain relievers for tooth sensitivity?
Yes, over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help with tooth sensitivity. Follow the dosage instructions and see a dentist if the pain continues.
6. Can fluoride treatments or gels provide instant relief?
Fluoride treatments or gels can help strengthen teeth and reduce sensitivity over time. While they may not give instant relief, they can protect teeth and lessen pain gradually.
7. Is there a specific mouthwash you recommend for fast pain relief?
Yes, a dental sealant or coating can help protect sensitive teeth and reduce pain. However, it requires a dentist’s application and may not provide instant relief.
8. Would a dental sealant or coating help reduce my sensitivity quickly?
Yes, a dental sealant or coating can help reduce sensitivity by protecting the tooth. However, it needs to be applied by a dentist and may take some time to work.
9. When should I come in for an emergency visit if the pain doesn’t stop?
If the pain is severe, lasts more than a day, or comes with swelling or fever, see a dentist immediately. It could be a sign of a serious problem needing urgent care.
10. Could my tooth sensitivity be a sign of a more serious problem that needs immediate attention?
Yes, tooth sensitivity can be a sign of cavities, gum disease, or nerve damage. If the pain is severe or lasts long, see a dentist as soon as possible.

